
Unconformities are erosional surfaces that represent gaps in geologic time between the formation of the lower rock surface and the overlying sedimentary or volcanic layers.If fragments of one rock type are observed as inclusions within another rock type, the first rock type had to exist prior to the rock type that hosts its inclusions.The law of faunal succession states that fossil species succeed one another in undisturbed rocks in a definite and recognizable order around the world. Law of Superposition - which states that, in any undisturbed sequence of rocks deposited in layers, the youngest layer is on top and the oldest on bottom.This rule applies also to mass wasting and erosion whatever is eroded had to exist prior to the beginning of erosion. Any rock that cross‐cuts another rock is younger than the rock it cross‐cuts.Any layered sequences that are now tilted were moved by later geologic processes.
#IN AN UNDISTURBED SEQUENCE OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS SERIES#
It states that if a series of layered sediments have. Explanation: Sedimentary rocks are formed when sediments are compressed under their own weight for a large period of time.

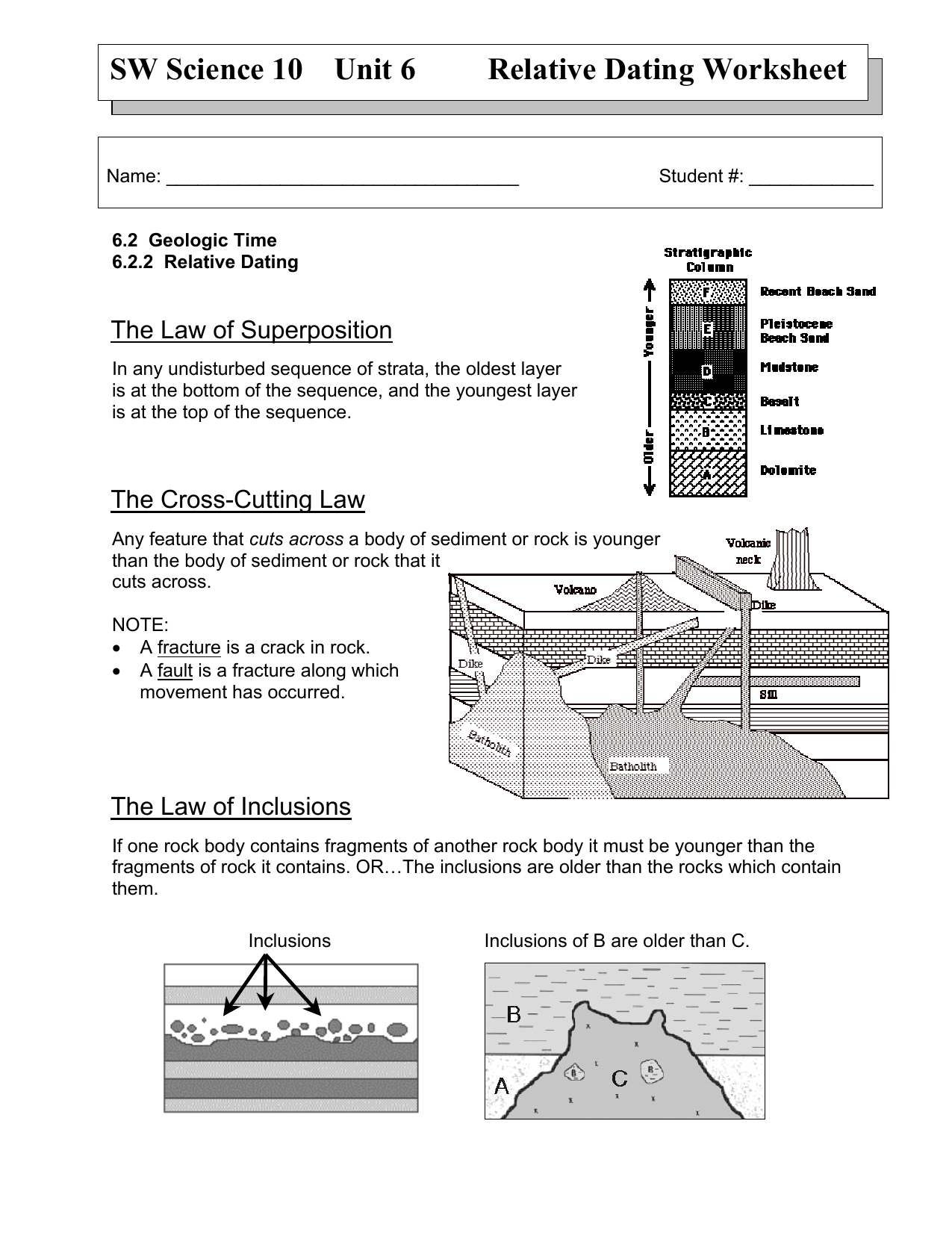
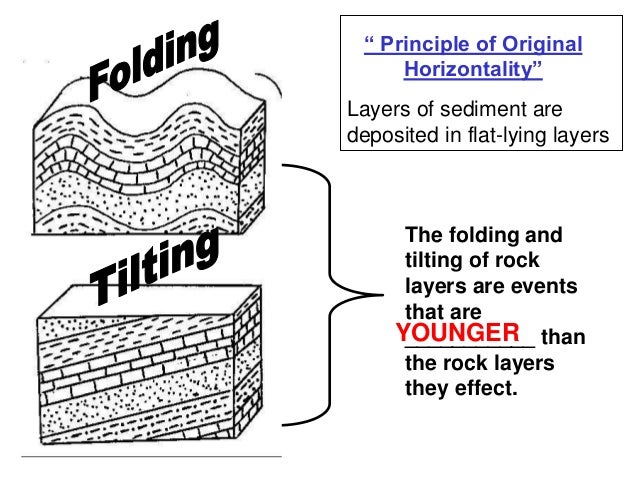
As previously described in this book, geologists use some basic, simple principles to unravel “which came first”:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
